Overview of the Nepal Floods
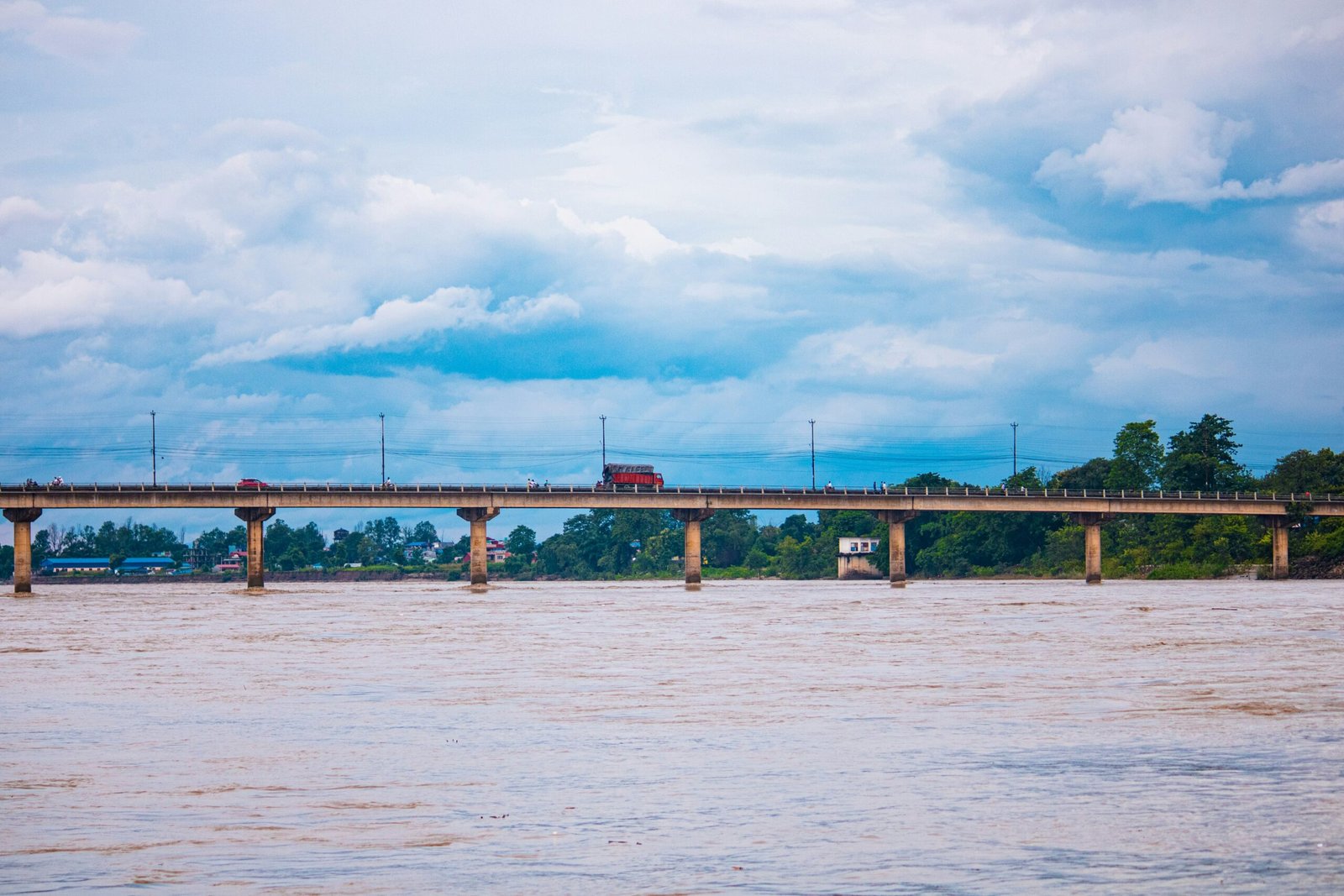
In the months leading up to October 2023, Nepal faced a severe natural calamity as flooding wreaked havoc across the country. These floods were primarily triggered by unusually heavy monsoon rains that occurred over a short period, which overwhelmed the local water management systems. The most affected regions included provinces such as Bagmati, Gandaki, and Lumbini, where rivers overflowed their banks, inundating villages and urban areas alike.
The immediate consequences of this disaster were devastating. Thousands of households found themselves submerged, leading to significant displacement of the population. Reports indicated that over 100,000 individuals were forced to flee from their homes, seeking refuge in temporary shelters set up by local authorities and humanitarian organizations. The rapid onset of the floods left little time for preparation, exacerbating the situation for those caught in the disaster.
Infrastructure suffered substantial damage, with roads, bridges, and public utilities being washed away or severely compromised. This destruction not only hindered immediate rescue and relief efforts but also raised concerns about the long-term recovery of affected areas. Educational institutions and health facilities were also impacted, disrupting essential services that many communities rely on.
The scale of the flooding highlighted the vulnerability of certain regions in Nepal to extreme weather events. The natural disaster further exposed the need for robust disaster preparedness strategies and better infrastructure to manage water resources effectively. As the nation grapples with the aftermath, the focus will remain on recovery, rehabilitation, and reevaluating existing policies to mitigate future risks from natural disasters.
Casualties and Humanitarian Response
The recent floods in Nepal have inflicted a tragic toll on the nation, with confirmed casualties exceeding 170 individuals. The loss of life in such catastrophic natural disasters highlights the vulnerability of many communities situated in areas prone to flooding. The sheer scale of the devastation has prompted widespread concern and mobilization of resources for both immediate and ongoing relief efforts. Search and rescue operations have been conducted tirelessly by local authorities and rescue teams, focusing on locating missing persons and providing urgent medical assistance to those who have survived the initial deluge.
The government of Nepal, in collaboration with various non-governmental organizations (NGOs), has engaged in a multifaceted humanitarian response to address the desperate needs of affected communities. Immediate actions have included the establishment of temporary shelters for those displaced, ensuring that individuals have access to safe and secure locations while further assessments of the damage are underway. The provision of food and water is also a critical component of the relief effort, as many families have lost their homes and access to basic necessities due to flooding.
Additionally, medical assistance has been prioritized to tackle the imminent health risks posed by the floods, including waterborne diseases which could arise in the aftermath of such disasters. Medical teams have been deployed to offer healthcare services, distribute essential supplies, and monitor public health conditions. The cooperation among governmental and non-governmental entities is vital to ensure a coherent and effective approach to recovery in the face of adversity. Community involvement has also been instrumental, as local volunteers and organizations coordinate with government agencies to facilitate aid distribution and provide emotional support to those affected by the tragedy.
Long-Term Effects on Communities
The recent floods in Nepal have left an indelible mark on the affected communities, leading to a range of long-term effects that will take years to fully understand and address. One of the most immediate impacts is the psychological toll on survivors. Many individuals and families have experienced profound trauma from the loss of loved ones, homes, and livelihoods. Mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder, are likely to become endemic in these regions, necessitating the availability of support systems to aid recovery.
Economically, the repercussions are significant for families and local businesses. The destruction of homes and infrastructure has led to an immediate loss of income, particularly for those dependent on agriculture, a primary livelihood source in rural areas. Farmers face the dual challenge of rebuilding their livelihood while also managing the loss of crops and livestock. Local businesses, already fragile due to previous economic challenges, now confront a diminished customer base and increased operating costs as they rebuild. This combination could lead to longer-term economic decline in these regions, further escalating poverty levels.
Challenges in rebuilding homes and infrastructure also present long-lasting effects. The process of reconstruction often requires extensive resources, funding, and skilled labor, all of which may be in short supply following a disaster. Temporary housing solutions are frequently inadequate, leading to overcrowding and compounding vulnerability to future disasters. Furthermore, essential services such as education and public health may suffer in the aftermath. Schools damaged by floods may take time to reconstruct, impacting children’s education and future opportunities. Similarly, public health services may become strained, increasing the risk of disease outbreaks during recovery periods.
In conclusion, the long-term effects of the recent floods in Nepal will undoubtedly shape the course of recovery for the communities involved. Addressing the psychological, economic, and infrastructural challenges will be essential for fostering resilience and promoting sustainable development in the wake of such a tragic event.
Climate Change and Future Preparedness
The recent floods in Nepal have underscored the quintessential link between climate change and the increasing frequency of natural disasters. Extreme weather events, such as torrential rainfall and subsequent flooding, have become more commonplace, challenging existing disaster response frameworks. The geographical vulnerabilities of Nepal, including its mountainous terrain and dense river networks, exacerbate the situation as shifting weather patterns due to climate change contribute to unpredictable and severe flooding.
In response to the changing environmental landscape, there is a pressing need for enhanced disaster preparedness strategies. This entails not only the establishment of robust early warning systems but also investment in infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather conditions. Current systems often struggle to effectively relay information in a timely manner, thereby increasing the risk to vulnerable communities. Improving these systems requires collaboration between government agencies and local organizations to ensure that warnings are disseminated quickly and effectively to those most at risk.
Community education is another critical component of future preparedness. By informing the general population about flood risks and encouraging proactive measures, Nepal can significantly enhance its resilience against climate-related disasters. Educational programs should focus on basic survival strategies during floods, as well as promoting sustainable practices that reduce environmental impact. Engaging communities in climate adaptation initiatives will empower them to take ownership of their safety and security, ultimately contributing to a culture of resilience.
Additionally, incorporating climate change adaptation policies into national planning is essential. Integrating climate projections into development strategies will help mitigate future risks. By understanding the connection between climate change and natural disasters, Nepal can create frameworks that not only respond to the current crises but also prepare for the uncertainties ahead. The path forward necessitates a concerted effort to adapt to a changing climate and bolster community preparedness against the inevitable challenges that lie ahead.